Measles: Understanding an Enduring Challenge:
Measles: Understanding an Enduring Challenge:
Introduction:
Measles may be an exceedingly irresistible viral illness known for its striking ruddy hasty and fever. In spite of being preventable through inoculation, it remains a noteworthy open well being challenge around the world. This article digs into the history, pathology, and societal effects of measles, highlighting the significance of continued endeavors in immunization and open well being procedures to combat this persistent malady.
The History of Measles:
Origins of the Disease:
It has tormented mankind for centuries, with depictions back to the 7th century. The disease’s capacity to cause wide plagues was recognized early in history, underscoring the require for practical control measures.
Significant Outbreaks in History:
Recently, with the advancement of immunization, measles caused standard scourges, annihilating communities. The 20th century saw critical episodes, especially in populations without a past introduction, illustrating the disease’s dangerous potential.
The Development of the Measles Vaccine:
The measles immunization, developed in the 1960s, marked a turning point in against the infection. Its presentation is driven by a sensational decrease in cases and passings, displaying the vaccine’s role as a basic device in measles control.
Understanding Measles:
Causative Agent:
The measles infection, a part of the class Morbillivirus, is the disease’s causative specialist. It’s profoundly irresistible, spreading through respiratory beads and coordinating contact with a contaminated individual.
Transmission and Spread:
Measles is known for its effective transmission, with each contaminated person possibly spreading the infection to nine to 18 others without insusceptibility. It spreads through airborne particles and bead contact, flourishing in close-living conditions.
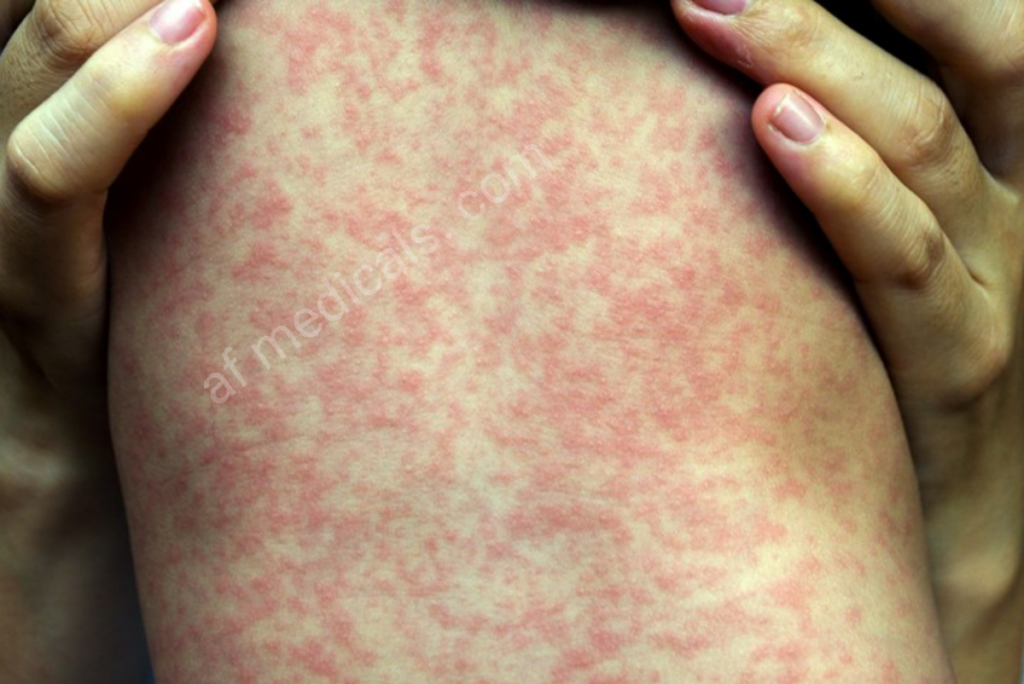
Clinical Manifestations:
Symptoms of measles:
The starting indications incorporate fever, hack, runny nose, and conjunctivitis, taken after by the characteristic ruddy hasty. The hastiness regularly spreads from the face to the rest of the body.
Stages of infection:
It contamination advances through a few stages, beginning with a hatching period followed by the appearance of indications and, at last, the hasty. The whole handle underscores the virus’s effect on the body’s resistant framework.
Complications and Associated Risks:
Complications can be extreme, extending from loose bowels and ear diseases to pneumonia, encephalitis, and death. These complications are more common in children under five and adults over 30.
Diagnosis of Measles:
Clinical Diagnosis:
Determination is frequently based on characteristic side effects and haste. Be that as it may, in zones where measles is less common, research facility affirmation is pivotal for a precise conclusion.
Laboratory Tests:
Particular research facility tests, counting serology for its antibodies and PCR for viral RNA, can affirm measles contamination, giving fundamental data for open well being reactions.
Treatment and Management:
Supportive Care Measures:
There’s no particular antiviral treatment. Administration centers on diminishing indications and tending to complications, emphasizing the significance of strong care.
Managing Complications:
Complications require particular interventions, such as anti-microbials for bacterial diseases or hospitalization for extreme cases, highlighting the need for comprehensive restorative care.
Prevention and Control:
Vaccination:
The MMR immunization, which ensures against mumps and rubella, is the foundation of measles anticipation. Guaranteeing broad immunization scope is vital for controlling the disease.
Public Health Measures:
In addition to inoculation, open wellbeing measures such as segregation of cases, contact following, and keeping up with high levels of group insusceptibility are imperative for anticipating episodes.
Challenges in Eradication:
Vaccine Hesitancy and Refusal:
Immunization reluctance and refusal posture are noteworthy deterrents to measles control, indeed driving to episodes in nations with by and large high inoculation rates.
Access to Vaccination:
In low-income nations, getting inoculated remains a challenge, underscoring the need for worldwide well being activities to guarantee immunization accessibility.
The Social and Economic Impact of Measles:
Burden on Healthcare Systems:
Measles episodes put an overwhelming burden on healthcare frameworks, requiring noteworthy assets for reaction and administration.
Economic Costs:
The financial effects of measles incorporate healthcare costs and misplaced efficiency, highlighting the disease’s broader societal results.
Future Directions:
Advances in Vaccine Technology:
Investigate into making strides in immunization conveyance and adequacy may upgrade measles control endeavors, advertising trust for way better security against the malady.
Strategies for Improving Vaccination Coverage:
Imaginative procedures for expanding immunization scope, particularly in hard-to-reach populations, are fundamental to controlling measles.
Conclusion:
Measles could be a preventable malady that still poses a noteworthy danger to worldwide well being. Whereas inoculation has drastically diminished the rate of measles, continuous endeavors are required to reach the objective of worldwide annihilation. Open well being activities must center on keeping up the inoculation scope, observing for flare-ups, and guaranteeing that all communities have access to the measles antibody. Through collective global action and commitment, it is conceivable to make measles an infection of the past.






