Ischemic Heart Disease: A Comprehensive and Empowering Guide:
Ischemic Heart Disease: A Comprehensive and Empowering Guide:
Ischemic heart disease (IHD), moreover known as coronary supply course ailment (CAD), may be a condition characterized by a diminished blood stream to the heart muscle. This reducing within the blood stream is routinely due to the buildup of plaque interior the coronary courses, driving to atherosclerosis. IHD may be a driving cause of passing and inadequacy around the world, making it a essential run of considering around and open prosperity intervention.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Understanding Ischemic Heart Disease
- 2.1 Definition and Overview
- 2.2 Causes and Risk Factors
- 2.3 Pathophysiology
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- 3.1 Clinical Manifestations
- 3.2 Diagnostic Approaches
- Management and Treatment
- 4.1 Lifestyle Modifications
- 4.2 Pharmacological Treatment
- 4.3 Surgical Interventions
- Complications and Prognosis
- 5.1 Acute and Chronic Complications
- 5.2 Prognosis
- Prevention and Public Health Strategies
- 6.1 Primary Prevention
- 6.2 Secondary Prevention
- Future Directions in Research and Treatment
- Conclusion
Introduction:
Ischemic heart disease could be a driving cause of passing around the world, influencing millions of people. In spite of headways in therapeutic science and treatment modalities, the predominance of IHD remains high, requiring a more profound understanding of its components, hazard variables, and effective administration procedures. This article points to a careful diagram of IHD to educate both healthcare experts and the public about its centrality, challenges, and the progressing endeavors to combat it.
Understanding Ischemic Heart Disease:
2.1 Definition and Overview:
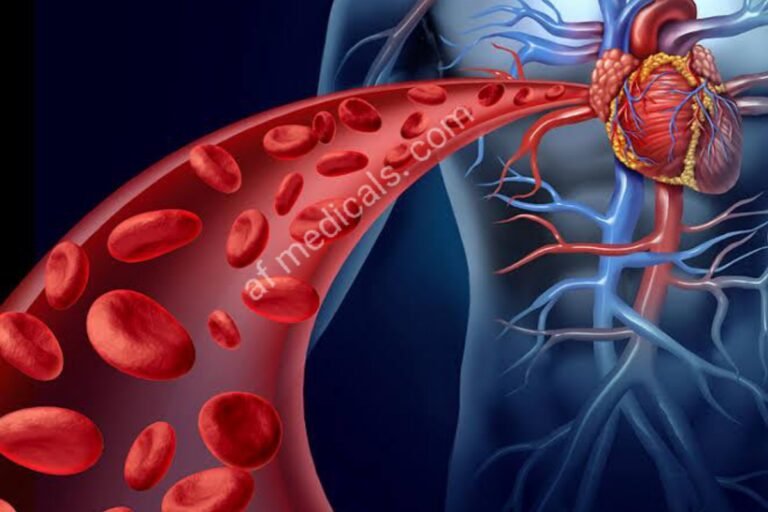
IHD happens when there’s a jumble between the oxygen supply and demand of the heart muscle, basically due to hindrance or narrowing of the coronary courses by atherosclerotic plaques. This condition can lead to angina, myocardial dead tissue, and possibly death.
2.2 Causes and Risk Factors:
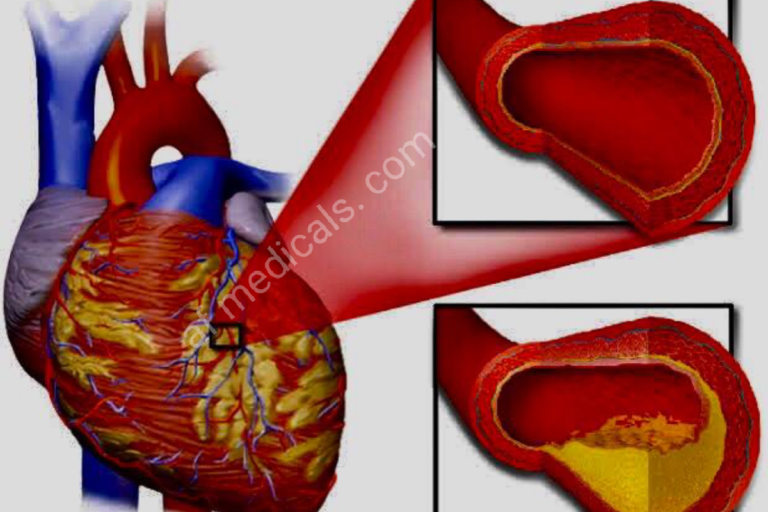
The essential cause of IHD is atherosclerosis, characterized by the buildup of greasy deposits inside the coronary supply routes. Hazard components incorporate undesirable way of life choices (such as smoking, destitute counting calories, and the need to work out), tall blood weight, high cholesterol, diabetes, weight, and hereditary inclination.
2.3 Pathophysiology:
The pathophysiology of IHD includes the dynamic narrowing of coronary courses, a lessening blood stream, and oxygen supply to the heart muscle. This can be regularly exacerbated by the cracking of atherosclerotic plaques, leading to thrombosis and intense coronary events.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
3.1 Clinical Manifestations:
Indications of IHD can range from none (quiet ischemia) to chest torment (angina), shortness of breath, weariness, and, in serious cases, heart assault. Angina is regularly activated by physical effort or passionate stretching and is soothed by rest or nitroglycerin.
3.2 Diagnostic Approaches:
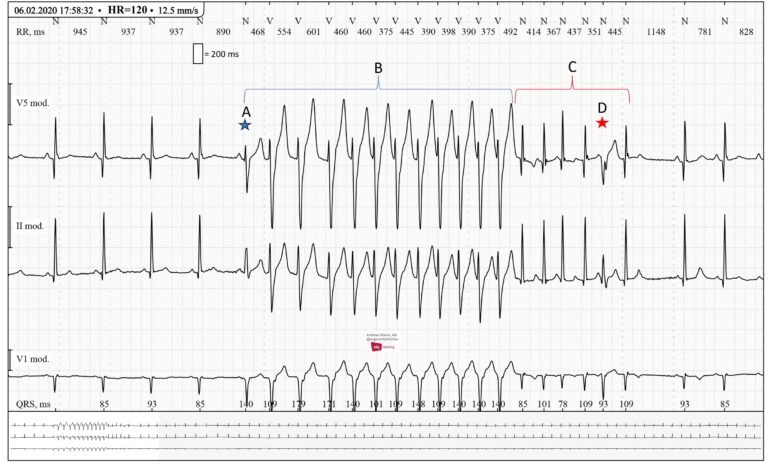
The determination of IHD includes a combination of understanding history, physical examination, electrocardiography (ECG), stretch testing, echocardiography, and coronary angiography. These apparatuses offer assistance in evaluating the seriousness of illness and direct treatment planning.
Management and Treatment:
4.1 Lifestyle Modifications:
Overseeing IHD incorporates critical life changes, such as receiving a heart-healthy count of calories, locking in standard physical movement, stopping smoking, and overseeing push, which can help moderate the movement of the infection.
4.2 Pharmacological Treatment:
Pharmacological treatments aim to calm side effects, oversee chance variables, and avoid complications. Common solutions incorporate ibuprofen, statins, beta-blockers, pro-inhibitors, and nitroglycerin.
4.3 Surgical Interventions:
In cases where pharmaceutical and way of life changes are lacking, surgical mediations like percutaneous coronary mediations (PCI) and coronary supply course bypass joining (CABG) may be essential to reestablish the blood stream to the heart.
Complications and Prognosis:
5.1 Acute and Chronic Complications:
The complications of IHD extend from intense myocardial dead tissue and sudden cardiac passing to incessant conditions like heart disappointment and arrhythmias.
5.2 Prognosis:
The guess of IHD shifts based on the degree of coronary supply route infection, the adequacy of treatment, and the nearness of other comorbid conditions. Early discovery and comprehensive administration are significant for making strides.
Prevention and Public Health Strategies:
6.1 Primary Prevention:
Essential avoidance centers on controlling chance variables some time after the onset of illness through open wellbeing activities, way of life alterations, and pharmacotherapy for at-risk people.
6.2 Secondary Prevention:
Auxiliary avoidance targets people with built-up IHD, pointing to avoid illness movement and decrease the chance of repetitive cardiovascular occasions through forceful chance figure administration and restorative treatment.
Future Directions in Research and Treatment:
Developing inquire about within the field of IHD is investigating novel demonstrative instruments, restorative operators, and mediation methodologies, counting regenerative medication, exactness medication, and the utilization of progressed imaging methods. These advancements hold a guarantee for upgrading our understanding and administration of IHD.
Conclusion:
Ischemic heart disease remains a critical challenge to worldwide well being, requiring continued endeavors in investigation, open well being, and clinical hone to decrease its burden. Through comprehensive avoidance procedures, early discovery, and viable administration, the effects of IHD can be moderated, improving the quality of life and results for influenced people.