Angioplasty: Type,procedure,Details&Recover:
What is Angioplasty?
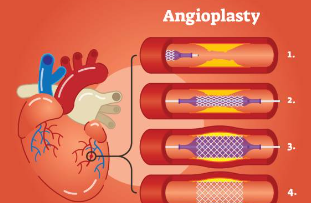
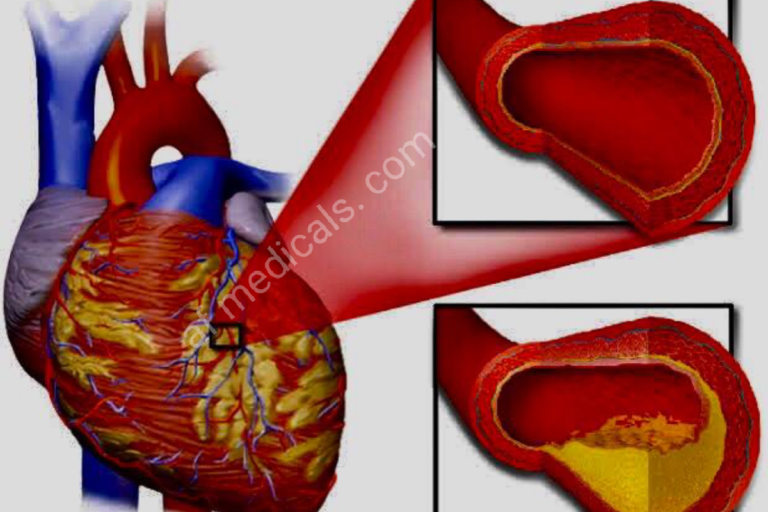
Angioplasty is a way used to unblock jammed coronary arteries caused by coronary artery diseases. It returns blood flow to the heart muscle without the need for open-heart surgery. Angioplasty should be thinkable in a disaster setting, for example, a coronary disaster. Or then again it tends to be performed as elective medical procedure in the event that your medical services supplier unequivocally thinks you have coronary illness. Angioplasty is likewise called per cutaneous coronary intercession .
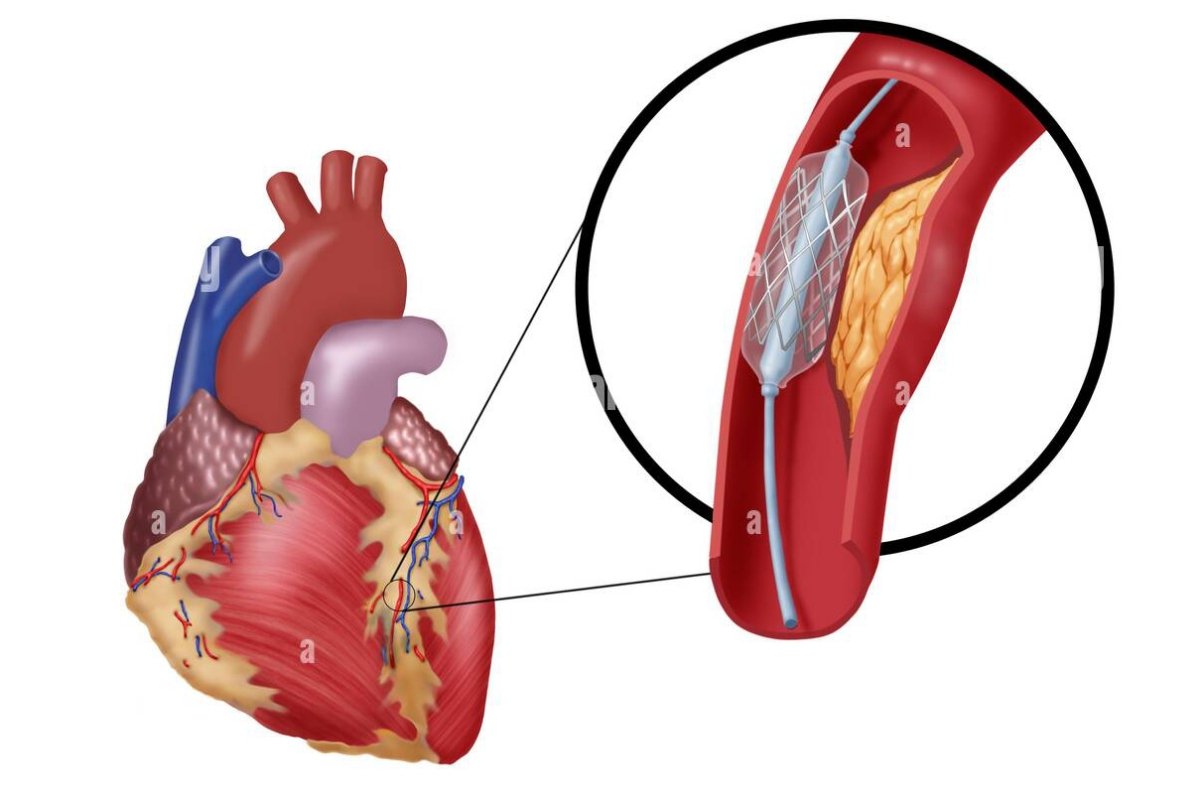
For angioplasty, a long, dainty cylinder (catheter) is placed into a vein and directed to the hindered coronary conduit. The catheter has a minuscule inflatable at its tip. When the catheter is set up, the inflatable is expanded at the limited region of the heart conduit. This presses the plaque or blood cluster against the sides of the corridor, setting aside more space for blood stream.
The medical care supplier utilizes fluoroscope during the medical procedure. Fluoroscope is a unique kind of X-beam that resembles a X-beam film. It assists the specialist with finding the blockages in the heart corridors as a differentiation color travels through the conduits. This is called coronary radiography.
The medical care supplier might conclude that you really want one more kind of technique. This might incorporate eliminating the plaque (hysterectomy) at the site of the restricting of the corridor. In hysterectomy, the supplier might utilize a catheter with a turning tip. At the point when the catheter arrives at the limited spot in the course, the plaque is separated or removed to open the conduit.
Whatis Stents?
Coronary stents are presently utilized in essentially all angioplasty strategies. A stent is a little, expandable metal lattice loop. It is placed into the recently opened region of the corridor to assist with holding the conduit back from limiting or shutting once more.
When the stent has been set, tissue will begin to cover the stent like a layer of skin. The stent will be completely fixed with tissue inside 3 to a year, in the event that on the off chance that the stent has a medication covering or not. You might be endorsed prescriptions called antiplatelet to diminish the “tenacity” of platelets. Platelets are exceptional platelets that cluster together to quit dying. The medication can likewise forestall blood clusters from shaping inside the stent. Your medical services group will give explicit directions on which medications should be taken and for how long.
Most stents are covered with medication to keep scar tissue from shaping inside the stent. These stents are called drug-eluting stents (DES). They discharge medication inside the vein that eases back the excess of tissue inside the stent. This keeps the vein from becoming limited once more. A few stents don’t have this medication covering and are called exposed metal stents (BMS). They might have higher paces of stenosis, however they don’t need long haul utilization of antiplatelet prescriptions. This might be the favored stent in individuals who are at high gamble of dying.
Since stents can become impeded, it’s vital to chat with your medical care group about what you want to do in the event that you have chest torment after a stent situation.
In the event that scar tissue structures inside the stent, you might require a recurrent strategy. This might be utilizing either swell angioplasty or with a subsequent stent. At times, radiation treatment might be given through a catheter put close to the scar tissue to stop the development of scar tissue and open up the vessel. This is called chemotherapy.
Why may I require an angioplasty?

Angioplasty is finished to reestablish coronary supply route blood stream when the restricted corridor is in a spot that can be arrived at thusly. Angioplasty cannot treat all coronary artery disease (CAD). Your primary care physician will choose the most effective way to treat your computer aided design in view of your conditions.
What are the dangers of angioplasty?
Possible risks linked to angioplasty& stenting:
- Bleeding at the site where the catheter is put into the body (usually the groin, wrist, or arm)
- Blood clot or damage to the blood vessel from the catheter
- Blood clot within the treated blood vessel
- Infection at the catheter insertion site
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Rupture of the coronary artery or complete closing of the coronary artery, needing open-heart surgery
- Allergic reaction to the contrast dye used
- Kidney damage from the contrast dye
You might want to inquire about the risks associated with your particular circumstance and the amount of radiation used during the procedure with your healthcare team. It is really smart to track your radiation openness, like past sweeps and different kinds of X-beams, so you can see your medical care group. Chances connected to radiation openness might be connected with the all out number of X-beams or therapies over an extensive stretch. Some people may experience some pain or distress as a result of having to remain still for the duration of the way on the procedure table. Dependent on your specific health condition, there may be added risks. Talk about any fears with your medical services group before the system.
How can I get ready for an angioplasty?
- Your healthcare team will explain the system to you and you can ask questions.
- You will be asked to sign a approval form that gives your leave to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if anything is unclear.
- Tell your healthcare team if you have ever had a return to any contrast dye, or if you are allergic to iodine.
- Tell your healthcare team if you are sensitive to or are allergic to any medicines, latex, tape, and local or general anesthesia.
- Follow any directions you are given for not eating or drinking before surgery.
- Tell your healthcare team if you are pregnant or think you could be. Radiation exposure through pregnancy may lead to birth faults.
- Tell your healthcare team if you have any body piercings on your chest or belly (abdomen).
- Tell your healthcare team of all medicine and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, herbs, and supplements that you are taking.
- Tell your healthcare team if you have a history of flow illnesses or if you are taking any blood-thinning medicines (anticoagulant or anti platelet), aspirin, or other pills that affect blood clotting. You may need to stop some of these medicines before the procedure. But for planned angioplasty processes, your doctor may want you to remain taking aspirin and anti-platelet treatments, so be sure to ask.
- Your breadwinner may request a blood test before the procedure to find out how long it takes your blood to clot. Other blood tests may be done as well.
- Tell your healthcare team if you have a pacemaker or other implanted device.
- You may get a sedative before the procedure to help you relax.
- Based on your health illness, your doctor may give you other instructions on how to get ready.
What happens in an angioplasty?
Angioplasty might be finished as a feature of your visit in a clinic. Methods might change relying upon your condition and your primary care physician’s practices. A great many people who have angioplasty and stent situation are checked for the time being in the medical clinic.
By and large, angioplasty follows this cycle:
- Any jewelry or other items that can obstruct the process will need to be taken off. If you use a hearing aid or dentures, you can wear them.
- You’ll be handed a robe to wear after being instructed to take off your clothes.
- Before the procedure, you will be asked to empty your bladder.
- Shaving may be necessary if there is a lot of hair at the site of the catheter insertion, which is frequently the groin region.
- Prior to the handling, an IV (intravenous) line will be inserted into your arm or hand. It will be used to administer IV fluids and administer medication injections, if necessary.
- On the treatment table, you will be laid flat on your back.
What occurs after angioplasty?
In the emergency clinic:
After the methodology, you might be taken to the recuperation space for perception or got back to your emergency clinic room. You will remain level in bed for a few hours after the methodology. A medical caretaker will screen your important bodily functions, the addition site, and flow and sensation in the impacted leg or arm.
Tell your medical caretaker immediately in the event that you feel any chest torment or snugness, or some other aggravation, as well as any sensations of warmth, dying, or agony at the addition site.
Bed rest might differ from 2 to 6 hours relying upon your particular condition. In the event that your PCP put a conclusion gadget, your bed rest might be more limited.
Now and again, the sheath or speaker might be left in the addition site. Assuming this is the case, the bed rest will be last until the sheath is taken out. After the sheath is eliminated, you might be given a quick bite.
You might want to pee frequently due with the impacts of the difference color and expanded liquids. You should utilize a chamber pot or urinal while on bed rest so your impacted leg or arm won’t be bowed.
After the predefined time of bed rest has been finished, you might get up. The attendant will assist you the initial time you with getting up, and will check your circulatory strain while you are lying in bed, sitting, and standing. You ought to move gradually while getting up to keep away from any discombobulating from the extensive stretch of bed rest.
You might be given torment medication for agony or uneasiness at the inclusion site or from being required to lie level regardless for quite a while.
You will be urged to hydrate and different liquids to assist with flushing the difference color from your body.
Unless your doctor tells you otherwise, you can resume your normal diet after the procedure.
After your method, you undoubtedly won’t leave the hospital for the night. Conditional upon your condition and the consequences of your methodology, your visit might be longer. You will get definite directions for your release and recuperation period.
At home
Once at home, screen the addition site for dying, strange agony, enlarging, unusual staining, or temperature change. A little injury is typical. Assuming you notice a consistent or enormous measure of blood at the site that can’t be held back with a little dressing, tell your medical care group.
On the off chance that your PCP utilized a conclusion gadget at your inclusion site, you will be provided explicit data in regards to the sort of a sense of finality gadget that was utilized and how to deal with the site. At the site, there will be a small knot or lump under the skin. This is typical. The bunch ought to gradually vanish north of half a month.
It will be vital to keep the inclusion site spotless and dry. Your medical care group will give you explicit washing guidelines. Generally, avoid be awash or using a hot tub until the skin has cured.
You might be exhorted not to take part in any arduous exercises. Your medical care group will teach you about when you can get back to work and resume ordinary exercises.
Inform your medical care team if you experience any of the following symptoms: Fever or chills – Increased pain, redness, swelling, bleeding, or other discharge from the insertion site Coolness, numbness, tingling, or other alterations in the affected arm or leg Chest pain or pressure, nausea, vomiting, excessive sweating, dizziness, or fainting Your primary care physician may provide you with specific instructions post-procedure based on your individual situation.
Subsequent stages:
Before you consent to the test or the strategy ensure you know:
- The name of the test or procedure
- The reason you are having the test or procedure
- What results to expect and what they mean
- The risks and benefits of the test or procedure
- What the possible side effects or complications are
- When and where you are to have the test or procedure
- Who will do the test or procedure and what that person’s qualifications are
- What would happen if you did not have the test or procedure
- Any alternative tests or procedures to think about
- When and how you will get the results
- Who to call after the test or procedure if you have questions or problems
- How much you will have to pay for the test or procedure